이전글 : [리액티브 코프링] R2DBC 사용법 (데이터 저장 & 수정)
모든 예제 코드는 필자의 github 레포지토리 에서 확인할 수 있다.
4. 연관 관계 구현하기
R2DBC는 JPA같은 ORM이 아니므로 연관 관계 매핑을 지원하지 않는다.
R2DBC에서 연관 관계 매핑과 같은 기능을 사용하기 위해서는 개발자가 추가적으로 코드를 작성해줘야한다.
도메인 & 요구사항
본 예제에서는 스프링 부트 실전 활용 마스터 의 장바구니 예제를 차용하고 있다.
Cart, CartItem, Item 엔티티를 사용하고 있으며 연관 관계는 아래와 같다.
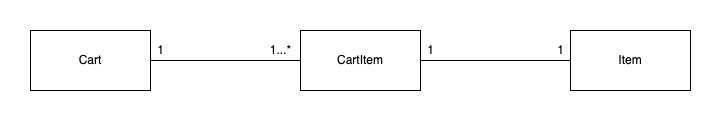
Cart와 CartItem은 1대 N 연관관계이고, CartItem과 Item은 일대일 연관관계이다.
엔티티 설정 (Transient)
데이터 조회편에서 엔티티를 선언했지만 연관 관계 구현을 위해 추가적으로 엔티티를 설정해줘야한다.
data class Cart(
@Id
val id: Long? = null,
@Transient
@Value("null")
var cartItems: List<CartItem>? = null
)
data class CartItem(
@Id
val id: Long? = null,
var quantity: Int = 1,
@Column("cart_id")
var cartId: Long? = null,
@Column("item_id")
var itemId: Long? = null,
@Transient
@Value("null")
var item: Item? = null
) {
fun increment() {
this.quantity += 1
}
}
data class Item(
@Id val id: Long? = null,
var name: String,
var price: Double
)이전의 엔티티와 차이가 있는데, @Transient 어노테이션 아래에 @Value("null")를 명시했다.
코틀린에서 R2DBC를 사용할 떄 @Transient를 적용한 프로퍼티에 기본값을 null로 할당했더라도 엔티티를 불러올 때 null값이 들어가지 않는 문제가 있다.
그래서 Cart에 cartItems가 없는 상황을 위해 @Value를 이용해서 null값을 넣어줘야 한다.
조회
엔티티를 수정했다면 Cart를 조회할 때 cartItems도 같이 조회하는 코드를 작성해보자.
@Repository
interface CartRepository : ReactiveCrudRepository<Cart, Long>, CartCustomRepository
interface CartCustomRepository {
fun getAll(): Flux<Cart>
fun getById(cartId: Long): Flux<Cart>
}
@Repository
class CartCustomRepositoryImpl(
private val dataBaseClient: DatabaseClient,
connectionFactory: ConnectionFactory
) : CartCustomRepository {
private val r2dbcEntityTemplate = R2dbcEntityTemplate(connectionFactory)
private val cartMapper: (t: MutableList<MutableMap<String, Any>>) -> Cart
get() {
val cartMapper: (t: MutableList<MutableMap<String, Any>>) -> Cart = { list ->
val cartId = list[0]["cart_id"] as Long
val cartItems = list.stream().map {
val id = it["id"] as Long
val quantity = it["quantity"] as Int
val cartId = it["cart_id"] as Long
val itemId = it["item_id"] as Long
val name = it["item_name"] as String
val price = it["item_price"] as Double
CartItem(
id = id,
quantity = quantity,
cartId = cartId,
itemId = itemId,
Item(
id = itemId,
name = name,
price = price
)
)
}.collect(Collectors.toList())
Cart(id = cartId, cartItems = cartItems)
}
return cartMapper
}
override fun getAll(): Flux<Cart> {
return dataBaseClient.sql(
"""
SELECT cart_item.*, item.name as item_name, item.price as item_price FROM cart
INNER JOIN cart_item ON cart.id = cart_item.cart_id
INNER JOIN item ON cart_item.item_id = item.id
"""
).fetch().all()
.bufferUntilChanged {
it["cart_id"]
}.map(cartMapper)
}
override fun getById(cartId: Long): Flux<Cart> {
return dataBaseClient.sql(
"""
SELECT cart_item.*, item.name as item_name, item.price as item_price FROM cart_item
INNER JOIN item ON cart_item.item_id = item.id
WHERE cart_item.cart_id = :cart_id
""".trimMargin()
)
.bind("cart_id", cartId)
.fetch().all()
.bufferUntilChanged {
it["cart_id"]
}.map(cartMapper)
}
}getAll() 동작 설명
- dataBaseClient.sql()를 이용해서 쿼리를 실행한다.
- 쿼리문은 cart, cart_item, item을 조인해서 item의 칼럼(name, price)과 cart_item의 칼럼(id, quantity, cart_id, item_id)을 불러온다.
- .fetch().all()로 쿼리를 실행하고 결과를 불러온다.
- bufferUntilChanged()를 이용해서 불러온 row 들을 cart_id 기준으로 묶어서 Flux<List
- map()을 이용해서 Map 형태로 받은 데이터를 엔티티로 변환해준다.
getById() 동작 설명
- dataBaseClient.sql()를 이용해서 쿼리를 실행한다.
- 쿼리문은 cart_item, item을 조인해서 item의 칼럼(name, price)과 cart_item의 칼럼(id, quantity, cart_id, item_id)을 불러온다.
- bind()로 쿼리문의 where 절에 넣을 cart_id 값을 입력해준다.
- bufferUntilChanged()를 이용해서 불러온 row 들을 cart_id 기준으로 묶어서 Flux<List
- map()을 이용해서 Map 형태로 받은 데이터를 엔티티로 변환해준다.
참고로, map()에서 사용하는 로직은 공통이라 cartMapper를 별도 선언해서 사용하고 있다.
그리고 bufferUntilChanged() 동작이 궁금하다면 본 글의 최하단 bufferUntilChanged() 관련 참고 자료를 참고하라.
저장
장바구니에 아이템을 넣는 동작을 구현해보도록 하자.
장바구니에 아이템을 넣는 동작은 두 가지 경우로 나뉜다.
- 장바구니에 넣을 아이템이 있는 경우
- 장바구니에 넣을 아이템이 없는 경우
1.의 경우에는 CartItem의 quantity만 1 증가시키면 된다.
2.의 경우에는 CartItem를 새로 생성하면서 quantity 값은 1로 초기화해준다.
위 동작을 구현한 코드를 보도록 하자
override fun addItemToCart(cartId: Long, item: Item): Flux<CartItem> {
// 1. 먼저 정의한 getById()로 cart를 조회한다.
return getById(cartId)
// 2. 만약 결과가 없다면 switchIfEmpty()로 Exception을 던진다.
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.error(RuntimeException("[cart not founded $cartId]")))
.flatMap { cart ->
// 3. 조회한 cart에서 추가할 item을 담고있는 CartItem을 찾는다. 만약, 없다면 새로운 CartItem을 생성한다.
val cartItem = cart.cartItems?.firstOrNull { it.itemId == item.id }
?: CartItem(
cartId = cartId,
itemId = item.id,
quantity = 0,
item = item
)
// 4. quantity를 1 증가시킨다.
cartItem.increment()
Mono.just(cartItem)
}.flatMap { cartItem ->
val id = cartItem.id
// 5-1. cartItem에 id가 있다면 update문으로 quantity 칼럼값을 업데이트한다.
if (id != null) {
r2dbcEntityTemplate.update(CartItem::class.java)
.matching(
org.springframework.data.relational.core.query.Query.query(
Criteria.where("id").`is`(id)
)
)
.apply(Update.update("quantity", cartItem.quantity))
.flatMap {
Mono.just(cartItem)
}
// 5-2. cartItem에 id가 없다면 insert 문으로 cartItem을 생성한다.
} else {
r2dbcEntityTemplate.insert(CartItem::class.java)
.using(cartItem)
}
}
}동작 설명
- 먼저 정의한 getById()로 cart를 조회한다.
- 만약 결과가 없다면 switchIfEmpty()로 Exception을 던진다.
- 조회한 cart에서 추가할 item을 담는 CartItem을 찾는다. 만약, 없다면 새로운 CartItem을 생성한다.
- quantity를 1 증가시킨다.
- 변경된 값을 DB에 반영한다.
- cartItem에 id가 있다면 update문으로 quantity 칼럼값을 업데이트한다.
- cartItem에 id가 없다면 insert 문으로 cartItem을 생성한다.
부록. 컨트롤러 구현
연관 관계 매핑 구현은 완료했다.
아래는 위 로직을 컨트롤러에 제공하기 위해 선언한 Service 객체의 코드이다.
@Service
class CartService(
val cartRepository: CartRepository,
val itemRepository: ItemRepository
) {
fun getAll(): Flux<Cart> {
return cartRepository.getAll()
}
fun getById(cartId: Long): Flux<Cart> {
return cartRepository.getById(cartId)
}
fun addItem(cartId: Long, itemId: Long): Flux<CartItem> {
return itemRepository.findById(itemId)
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.error(RuntimeException("item not founded $itemId")))
.flatMapMany { item ->
cartRepository.addItemToCart(cartId, item)
}
}
}아래는 CartService 객체를 사용하는 컨트롤러 코드이다.
@RestController
class CartController(val cartService: CartService) {
@GetMapping("v1/carts")
fun getCarts(): Flux<Cart> {
return cartService.getAll()
}
@GetMapping(value = ["v1/carts/stream"], produces = [MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE])
fun getCartsByStream(): Flux<Cart> {
return cartService.getAll()
}
@GetMapping("v1/carts/{id}")
fun getCartsById(@PathVariable("id") id: Long): Flux<Cart> {
return cartService.getById(id)
}
@PostMapping("v1/carts/{id}/add/{itemId}")
fun addItem(@PathVariable("id") cartId: Long, @PathVariable("itemId") itemId: Long): Flux<CartItem> {
return cartService.addItem(cartId, itemId)
}
}bufferUntilChanged() 관련 참고 자료
- https://javacan.tistory.com/entry/Reactor-Start-9-window-buffer
- https://www.vinsguru.com/reactor-buffer-vs-window/
연관 관계 구현하기 참고 자료
'리액티브 프로그래밍(Reactive Programming) > 리액티브 코프링' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [리액티브 코프링] R2DBC 사용법 (데이터 저장 & 수정) (0) | 2022.05.07 |
|---|---|
| [리액티브 코프링] R2DBC 사용법 (데이터 조회) (2) | 2022.05.03 |
| [리액티브 코프링] R2DBC 사용법 (들어가며) (0) | 2022.05.03 |